High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR)
It is possible to implement the senhasegura architecture using:
- PAM Crypto Appliances running into on-premises datacenters;
- PAM Virtual Appliances running into on-premises datacenters;
- PAM Virtual Appliances running into cloud providers;
High Availability Hardware
High Availability Hardware, have a heartbeat connection between the hardware components, assuring senhasegura turns to other hardware in case one of them suffers unavailability.
This architecture is designed to minimize interruptions in senhasegura caused by hardware failures. In this way, senhasegura provides continuity of services through high redundancy components.
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery involves a set of policies and procedures that allow the recovery of the infrastructure in case of disaster, natural or artificial. It enables the redefinition of senhasegura resources in an alternative environment when it is not possible to recover the primary environment in a reasonable time.
Replication technologies
There are many replication layers in senhasegura architecture to grant all data to be available in all senhasegura instances.
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Native database replication | senhasegura uses MariaDB Galera Cluster to grant database data replication, configured by default to support high latency networks |
| File system replication using rsync | All instances will echo their files between all cluster members |
| Kernel layer replication | When working with PAM Crypto Appliances, you also have a DRBD implemented |
Architectures
Active-Passive
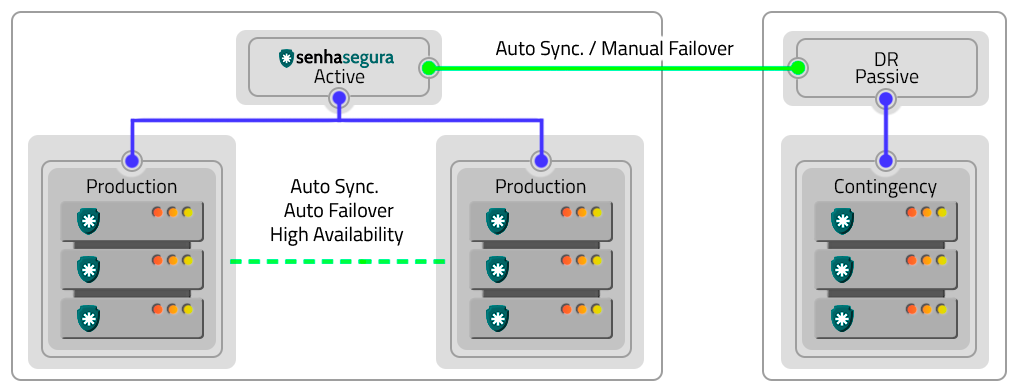
You can implement the Active-Passive schema using:
| scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Two PAM Virtual Appliances | |
| Two PAM Crypto Appliances | |
| Hybrid Scenario with PAM Crypto Appliances and Virtual Appliances | |
| Hybrid Scenario with on-premise and cloud instances |
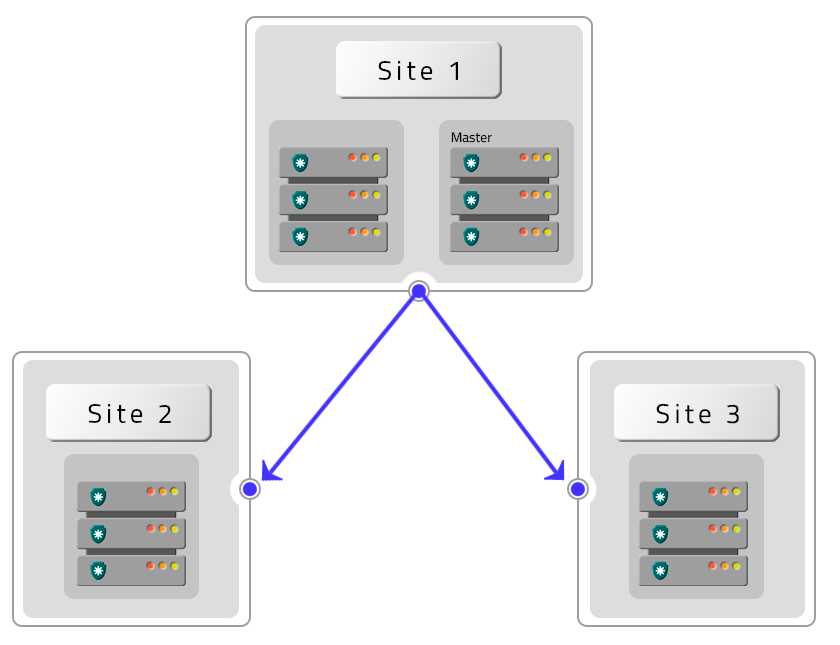
Active-Active
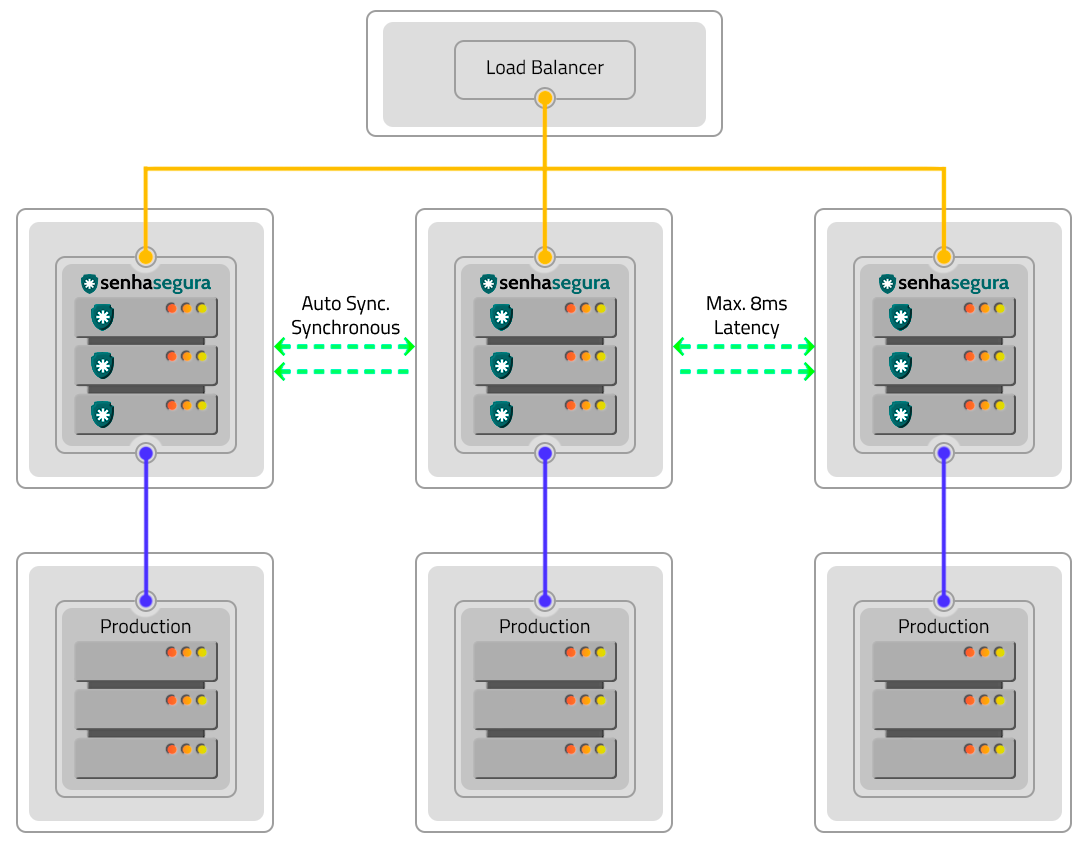
The Active-Active schema is a High Availability solution where multiple instances operate together, providing greater operational capacity and uninterruptible services.
By using this schema, the three applications will be active and in operation with synchronous automatic synchronization, executing processes in parallel. A load balancer will manage the distribution of work between the instances, besides ensuring the continuity of the service through the other instances, in case any of them stops working.
Disaster Recovery
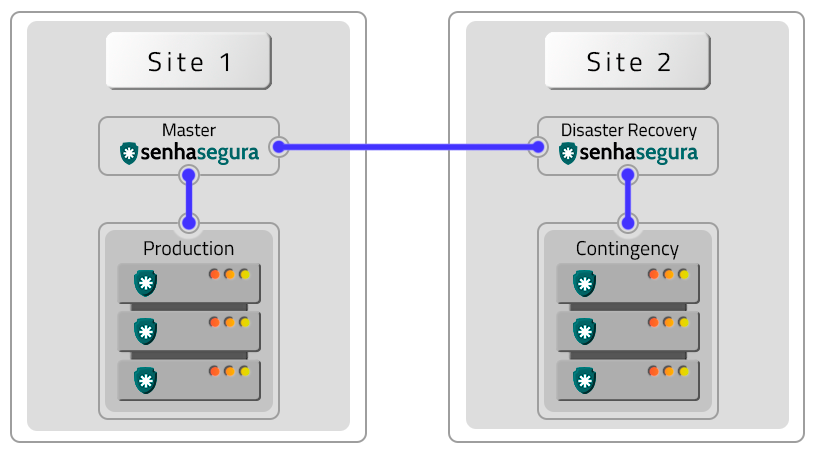
The Active-Passive schema avoids cluster and site failures. To implement it, two clusters in different locations operating in the Active-Passive schema are required. Factors such as DR and production environments influence the configuration and operation in this way.
The difference in data will depend on the quality and speed of the links in relation to the volume of data generated by a cluster. If these variables are not appropriate, there may be data loss, production environment shutdown and DR environment activation. In case of hardware failures, resetting and returning occurs manually.
Hot-Spare features and self-made Load balancer
senhasegura instances have monitoring and administrative URLs to monitor their status that load-balancers can use to switch instances into an unavailability scenario automatically.
You can use a proprietary load-balancer or acquire the senhasegura Load-balancer into your cluster scenario. See more at senhasegura Load-balancer manual.
Homologated Architectures
All architectures bellow can be deployed into hybrid schemas using on-premisse datacenters and cloud providers services.
The following architectures are homologated by senhasegura :
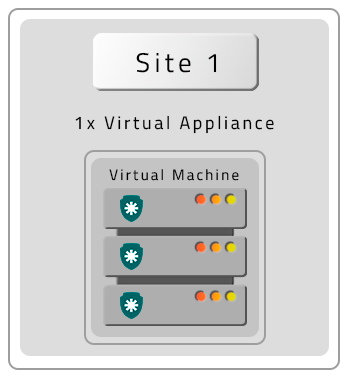
- A VM without Contingency (DR)
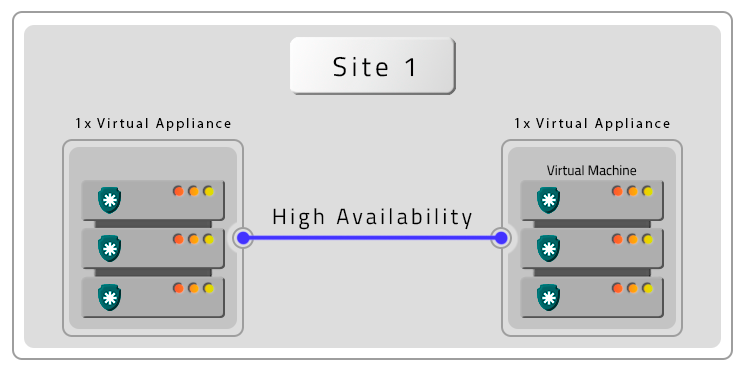
- Two VMs with contingency location (DR)
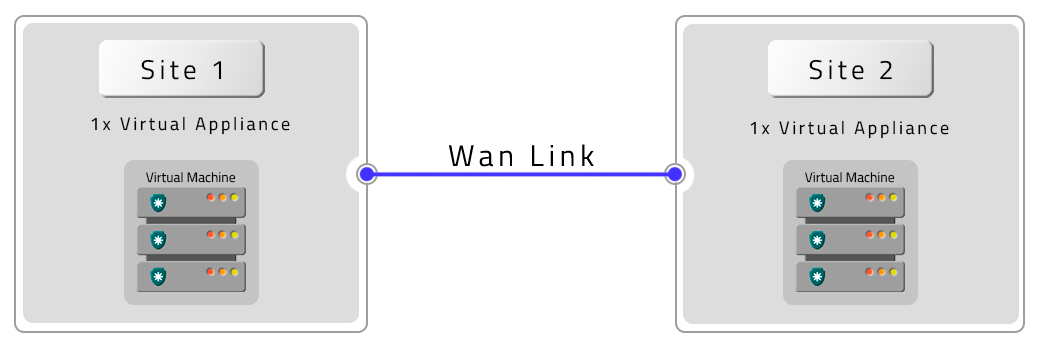
- Two VMs with Remote Contingency (DR)
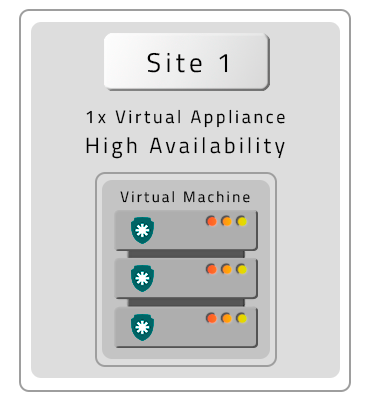
- A PAM Crypto Appliance without Contingency (DR)
- Two PAM Crypto Appliances in HA without contigency (DR)
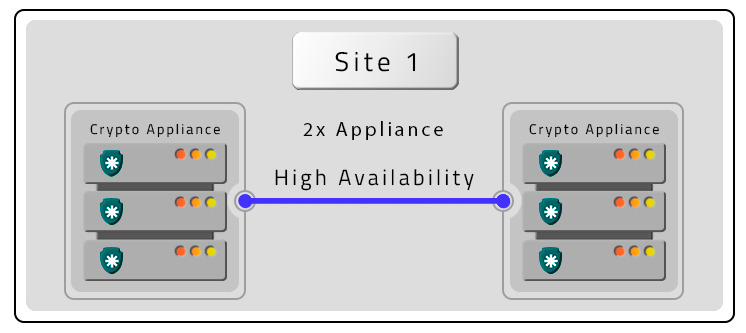
- Three PAM Crypto Appliances in HA and Contigency (DR) without HA
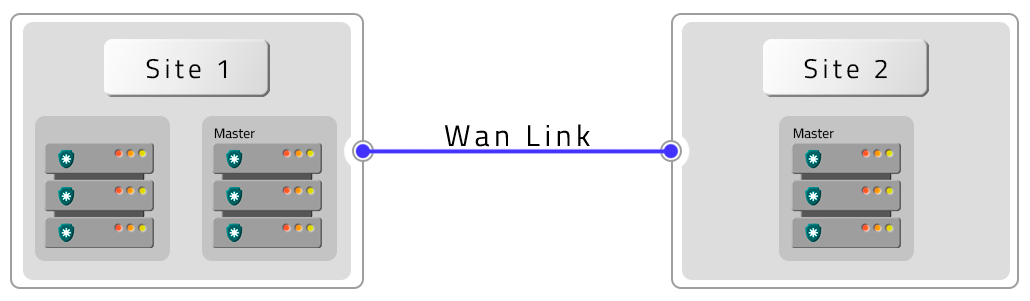
- Four PAM Crypto Appliances in HA with HA Contigency (DR)
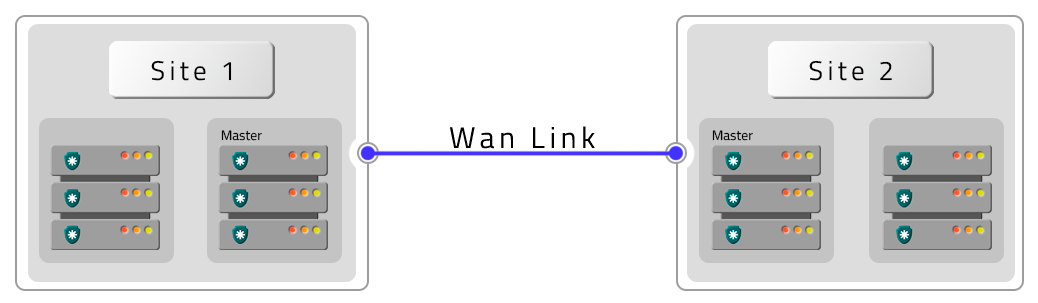
- Six PAM Crypto Appliances with HA and two DR with HA
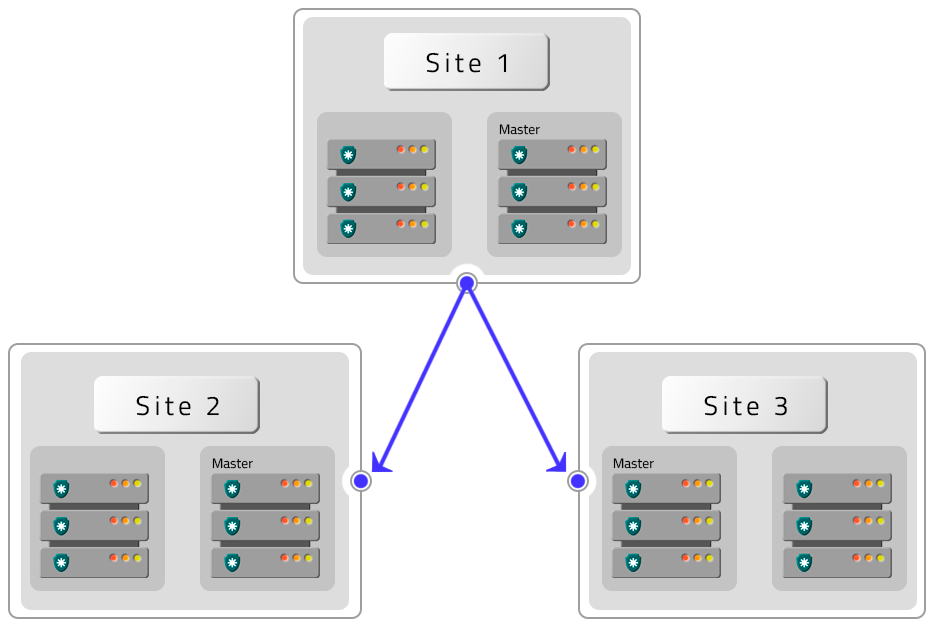
- Four PAM Crypto Appliances with HA with two DR without HA