Attempt Parameters and triggers
The triggers can be configured into the Password policies. And the attempts at the Execution Parameters.
Credential Policies
Credential policies are the point of union between password strength and credential. Plus settings about when the credential will have its password recycled and the intervals of these triggers.
You can find the credential policies through the PAM Core ➔ Settings ➔ Credentials ➔ Policy credentials menu.
The form for registering new policies resembles setting up Access Groups because its logic is similar. We will segregate some devices and credentials from their attributes. And then senhasegura will use the highest value of the Priority field if there is a policy tie.
Let's look at the Settings tab to identify how the use of the credential will be affected by the password policy.
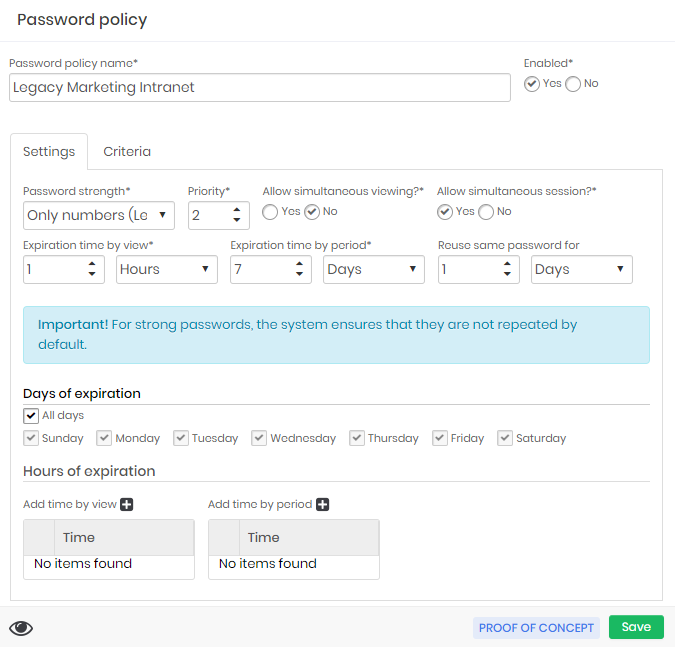
Note in the example that the policy created is to handle an old intranet system in the Marketing department. This system is using the password force Only numbers that was created especially for systems that accept only 5-digit numeric passwords.
Being a weak password, the administrator then decides to isolate the Marketing system in a security rule with the following configuration:
- Simultaneous Allow viewing?: The password withdrawal may not occur simultaneously. If a user performs the password withdrawal he will be in custody, and another user can only make the withdrawal if the user who holds custody releases the use;
- Simultaneous Allow session?: The users who want to perform proxy sessions with the credential will be able to perform simultaneous accesses since in these cases the password will not be exposed;
- Priority: Define the policy application priority if senhasegura finds more than one policy that applies to the credential. The higher the priority, the higher the number of this field;
- Expiration time by view: The time interval in which senhasegura will automatically change the password after viewing by a user. In this example, the password will be automatically changed after 1 hour of withdrawal;
- Expiration time by period: The time interval in which the password expires after a long period of no use. That is, no one used the password either via withdrawal or via proxy session. But the password must be recycled still;
- Reuse same password for: The time when the password will be reused after use by a proxy session. Unlike password withdrawal, when the password is used via proxy there is no direct exposure to the user. But it is recommended that the password be recycled after the proxy session. This interval then determines how long senhasegura should allow password reuse in other sessions until the automatic exchange is performed;
- Days of expiration: Some credentials cannot be recycled daily. Whether it's the security policies of the target device or the impacts it might have on the business. Then, in these fields you can configure which days the password exchange may occur;
- Hours of expiration: In the same way as the previous field, some deals only allow trading at certain times;
Note that all these fields determine actions that influence the customer's business rule, or target device security rules. Configuration mistakes of these fields can lead to the unavailability of the credential.
That's why it's very important to know and segregate target systems into dedicated password policies. Use the Criteria tab to perform segregation as you've already learned in the Access Group chapters.
See then that senhasegura immediately identifies the correct password policy to the credential at the time we link a device that matches the type and determine a credential with the tag configured.
If you change the password policy in a way that no longer applies to the credential, the credential will use a new policy that meets your device and credential characteristics.
To define the password change parameters in the vault, go to the menu Executions ➔ Settings ➔ Parameters. The following fields are available for adjustments:
- Number of change attempts: Number of times senhasegura will attempt to perform the operation in case of failure;
- Connection timeout (s): Maximum connection timeout, in seconds;
- Readout timeout (s): Maximum target output wait time, in seconds;
- Total records per cycle: Number of credentials to be considered for each cycle of automated execution;
- Interval between attempts (min): Interval, in minutes, between attempts to change a password that has given an error. Make this range suitable for devices that already have a history of high latency or intermittent outage. This interval refers to the attempts determined in the Number of change attempts field;
- Interval between attempts with error (min): If senhasegura runs out of attempts to change passwords, this execution will be marked as a failure and a new automated execution will only be performed within the interval determined by this field;
Click the Save button to complete the settings.