Chained operation automation
Automating password change operations allows users with administrator privileges to perform operations, such as password change linked, automatically or manually.
Linked execution is understood as an operation where the password of a target credential must be replicated to several different destinations. Sometimes containing different systems that require different executors and templates. For example: Ensuring that the database password is replicated for services hosted on Linux and Windows servers.
Using the automation script elaboration syntax, you can determine whether the operation will be performed when all credentials have been successfully changed, or even when only part of them have been successfully executed.
In the configuration of an execution script, it is possible to select the operation to be performed, as well as the strength of the changed passwords.
The run can also be configured to automatically on predetermined days and periods. You can also select a minimum interval between linked password change runs.
To exemplify its use in this document we will use the automation to run password change scripts, however this functionality can be used for any script.
SQL Linked Server
Using the senhasegura Operation Automation you can easelly change Microsoft®SQL Server Linked Servers passwords replicating accounts using senhasegura out-of-the-box templates for SQL Server instances.
senhasegura offers two different templates to deal with dynamic port configuration, or static port configuration.
When the SQL Server works with dynamic port configuration, you should configure the senhasegura device with the UDP port where SQL Server will publish which TCP port SQL Server is running in.
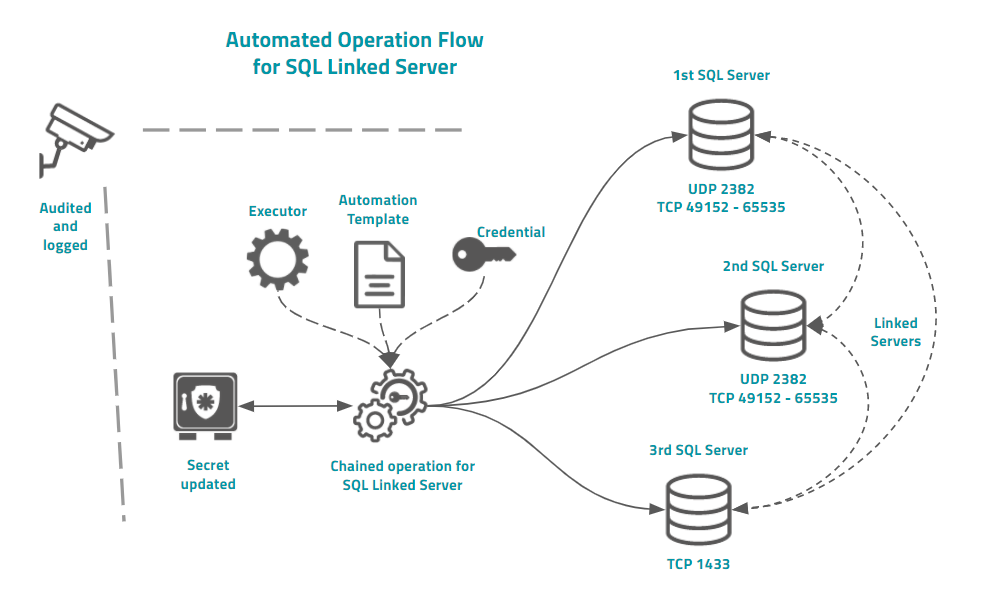
Into the example image you can see that this architecture are composed by two Microsoft®SQL Server instances running with Linked Server dynamic ports. So the device registered into senhasegura should have the UDP port configured.
senhasegura then will first query the UDP port for the right TCP port where the SQL Server is accepting database connections. So senhasegura will connect to this port to perform the template tasks.
Finished this first instance, and doesn't matter if it was successfully executed or not, senhasegura will then connect to the next server and go on.
The main difference between the use of chained operation and parent credentials is the fact that in chained operation you can use special syntax to determine which template should be replaced for Linked Server environments.
Register an automation
To register an automation, go to the menu Executions ➔ Operations automation ➔ Automations
- Click on the actions button and select the option New
- On the Settings tab, complete the following fields:
- Automation Name: Name. For internal control only
- Operation: type of automation. In this version, only the Chained exchange option will be available
- Password strength: Password strength used for automation. We recommend using the weakest device password policy so that you can be sure that all members of the chain receive the same password.
- Execution script: Script that makes up the chain of execution between devices
- Active?: Indicates whether automation is active for use or not
- In the Execution tab, fill in the following fields:
- Enable automatic execution?: Indicates whether automatic automation execution is active or not. If activated, the senhasegura will perform its execution from time to time
- Days to run: Automation will run on selected days of the week
- Execution periods: Automation will be performed within the selected periods
- Minimum interval between runs: Minimum interval between runs in hours
- Click the Save button to complete the settings.
The syntax of an automation script
The script will give the sequence by which each device will be reached. Therefore, it is important that you already have this information properly mapped before you start writing the script.
check_conn
Requires validating connectivity of target devices before starting the process. If the target device is not accessible, abort the operation. It contains no additional arguments and it is preferable that this command is at the beginning of the script.
rollback
Roll back the automation if any changes are not made. The rollback itself will be performed only at the end of the entire execution. That is, in an change of 10 credentials, if an error occurs in the fourth credential, it will still continue executing the others until the end and so it will rollback the entire operation.
This guarantees visibility to the administrator of which credentials are having problems.
In case the rollback command is not added, senhasegura will perform the change for all desired credentials but will not perform the rollback if an error occurs in one, some or all credentials.
linked_tpl uint: id
Determines which template will be used to change passwords when dealing with a Linked Server.
This causes the change template configured in the credential to be ignored and replaced by the template designated in the script.
The parameter id is a positive integer referring to the Id of the desired template.
change string: type uint: id string: is_linked
Changes the Credential or Pool of credentials, determined by the parameters type and id.
If the parameter is_linked is filled with linked, the template determined by the command linked_tpl will be used for the change.
The parameter type can vary between cred for when the value of id is the Id of a credential, or pool when the value of id is the Id of a credential pool.
The id parameter will always be a positive integer.
Look at the example below for better understanding.
## Lines started with sharp are comment
## Force connectivity validation before usage
check_conn
## Sets the linked server template.
## Its will use the template id 87
linked_tpl 87
## Sets the rollback flag
rollback
#### Sets the credential's or pool's change chain
## Change credentials 120 to 122.
## But credential 122 must use linked server template
change cred 120
change cred 121
change cred 122 linked
## Change credential pool 42 and 45
change pool 42
change pool 45
Perform an automation
To perform automation, go to the menu Executions ➔ Operations Automation ➔ Automation.
Click on the Run button. The automation of operations will be scheduled and the user will be able to follow the result in the menu View executions, described below.
View runs
To view the automation execution history, go to the menu Executions ➔ Operations Automation ➔ Executions.
On this screen, you can view various information on automation executions, such as number of operations performed, the result of the execution, if processed, ended in error, as well as the requesting user and the execution date of the request.
Click on the View operations button to get more details on the result of your operation. Each record on this screen corresponds to the execution of each target credential.
When the script is configured to run a Credential Pool, each credential in the pool will be shown record by record.