Microsoft Active Directory Authentication and Users Synchronization
Once user authentication is configured to be performed on the costomer's LDAP server, it is now necessary to configure which servers will be asked at the time of authentication.
Also, it is interesting that there is a synchronization of the users of the LDAP server in senhasegura .
Although senhasegura always checks the password and the user's status at the time of login, other user attributes can determine the level of permission within senhasegura . Thus, senhasegura from time to time will perform synchronization to normalize the registration fields and correctly allocate the user in the access groups and access profile of senhasegura .
There are a few premises for the administrator to configure this synchronization:
Be aware of how Access Groups and Access Profiles of senhasegura works;
Know how to register device and credential;
Receive a credential with query access to the destination LDAP that will be used by senhasegura to perform synchronization;
Best practices for authentication availability
senhasegura can be configured to authenticate to more than one LDAP server. But some architectures bring more performance and availability at the time of login. Because senhasegura composes the client's security strategy, it must have less impact at the time of login. Look at the following architectures and understand the risks and benefits of each.
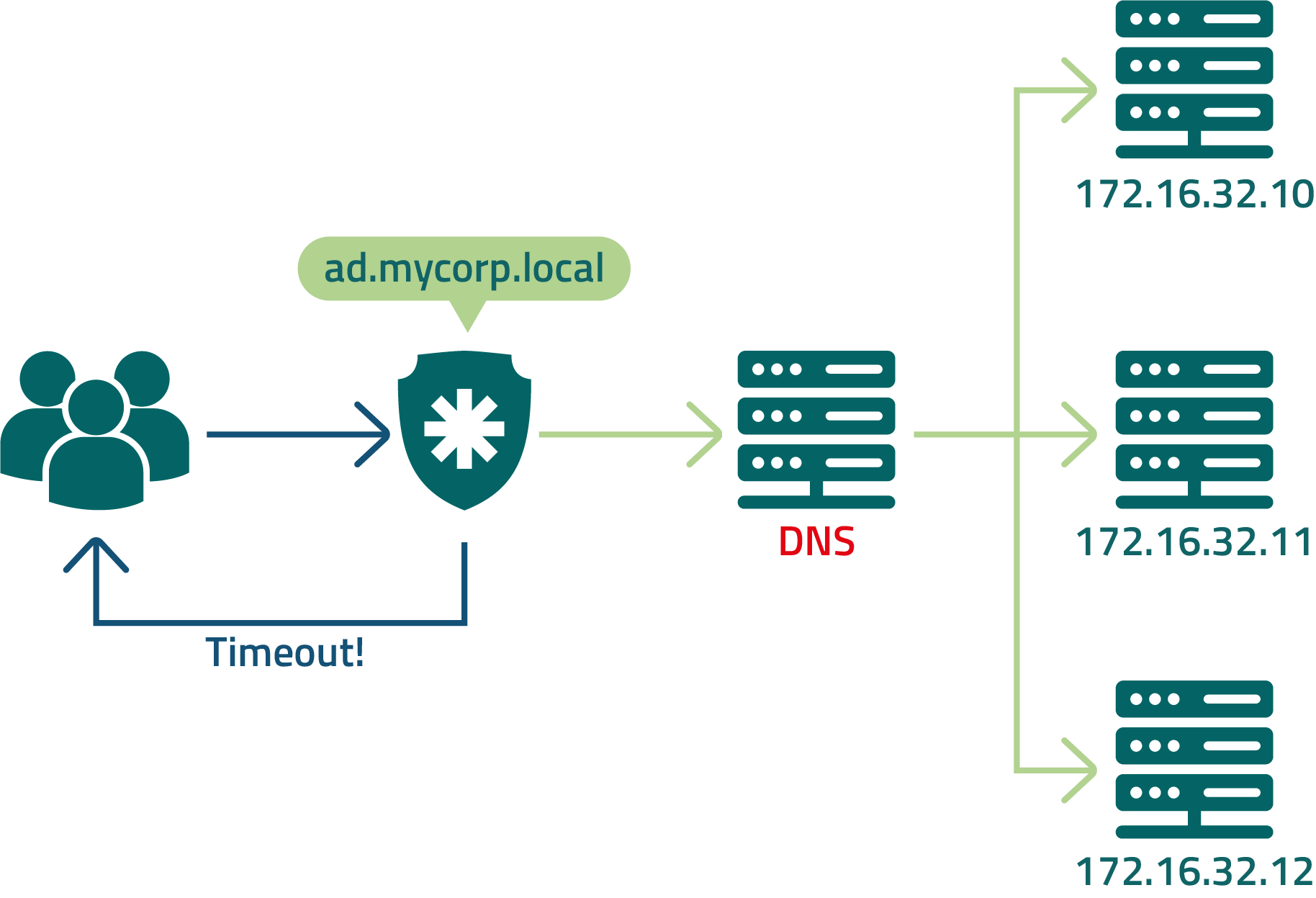
In this example, senhasegura is configured to query DNS to resolve the LDAP address being balanced by the load balancer.
Despite the ease of configuration, users may not be able to log in to senhasegura if the DNS server is unavailable.
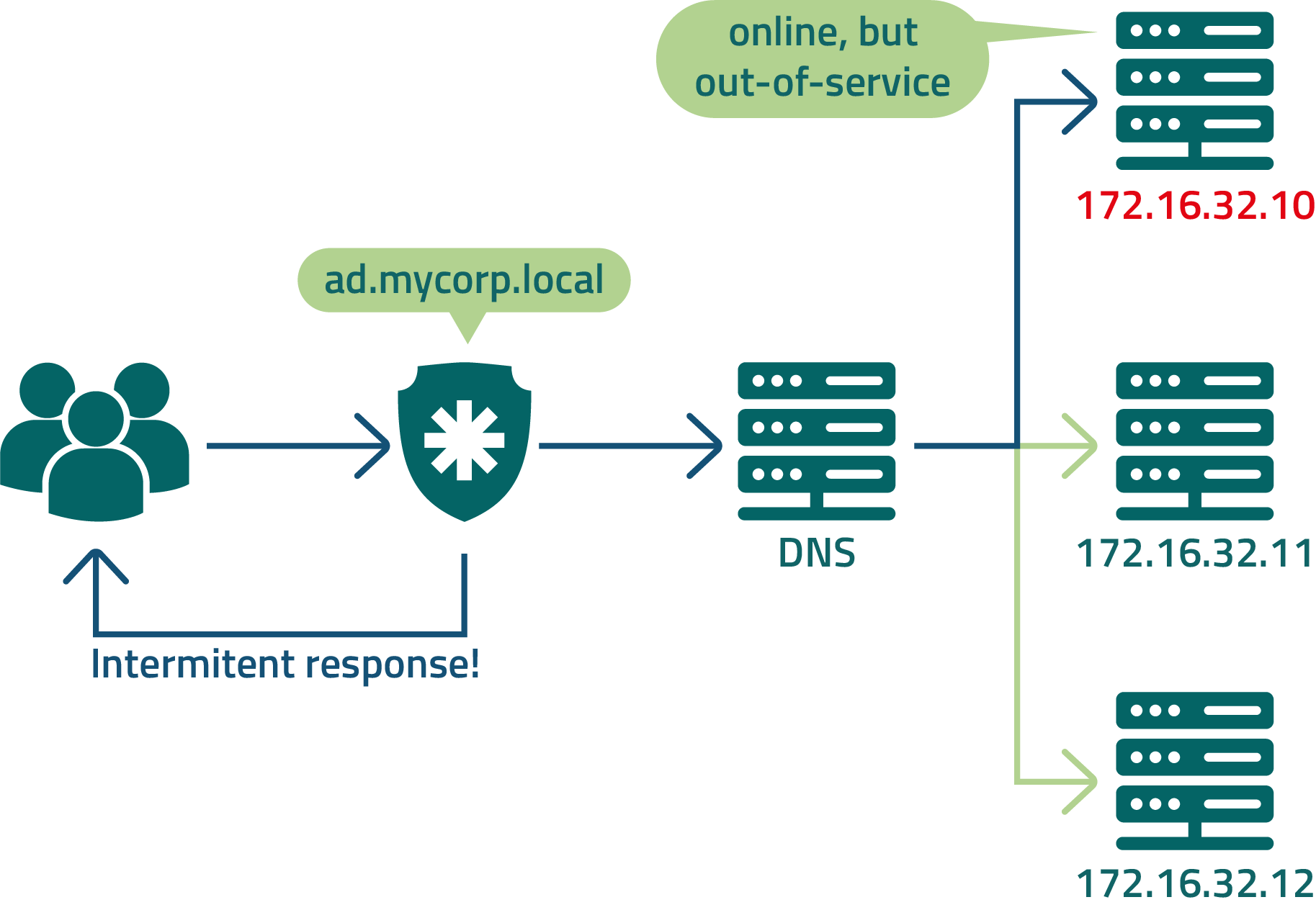
Sometimes the LDAP cluster member is unavailable for query, but the load balancer is not yet aware of this outage. In those cases, the user may receive an intermittent authentication attempt.
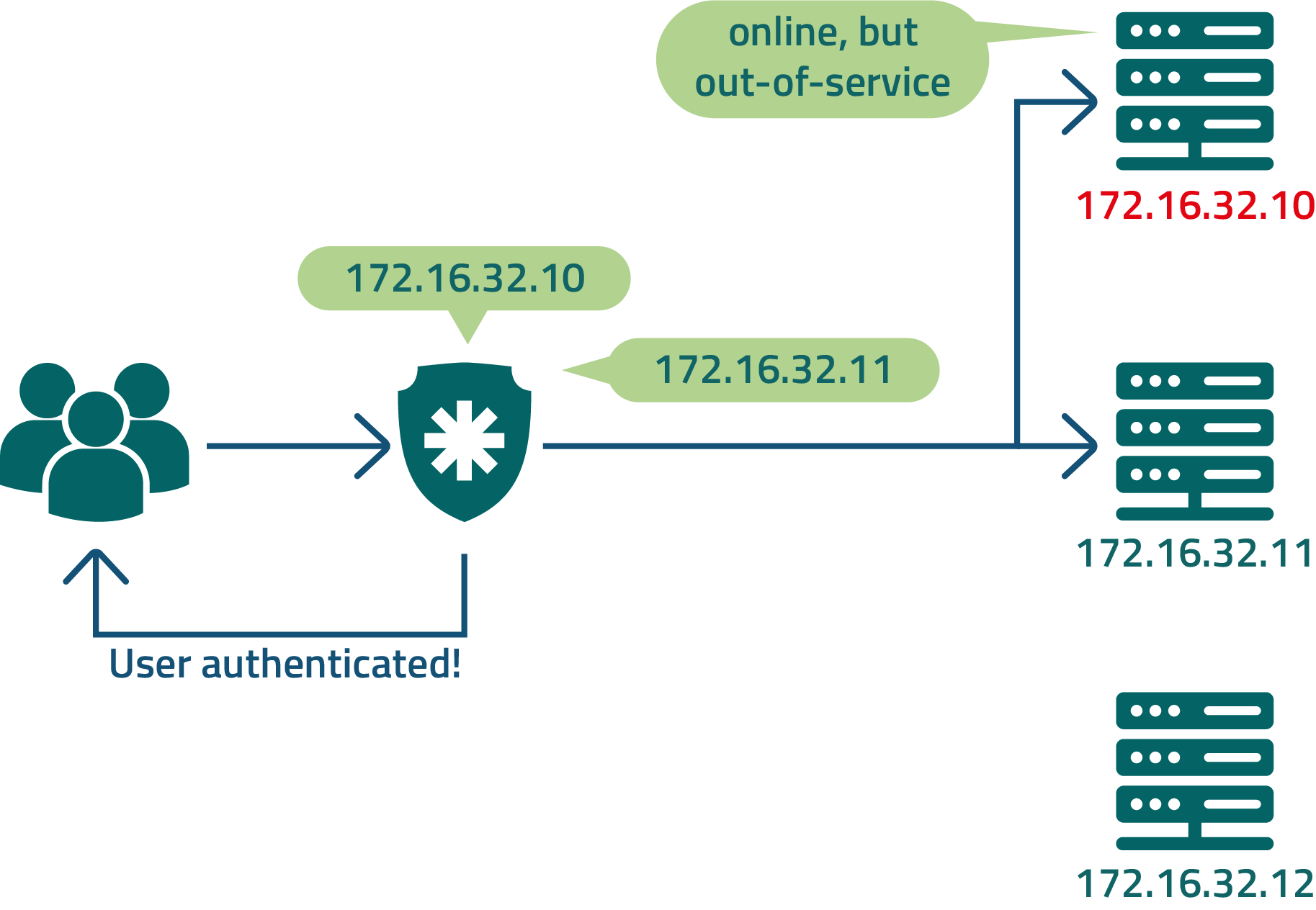
As a suggestion to avoid the cases described above, you can shorten the jumps and mitigate the risks present for DNS usage and a load balancer by registering all LDAP cluster members directly in senhasegura .
senhasegura will manage the sequence of inquiries. And if any member does not respond to the request, the next server will be asked.
Check with the customer about what will be the order of servers so it does not affect usage by other applications.
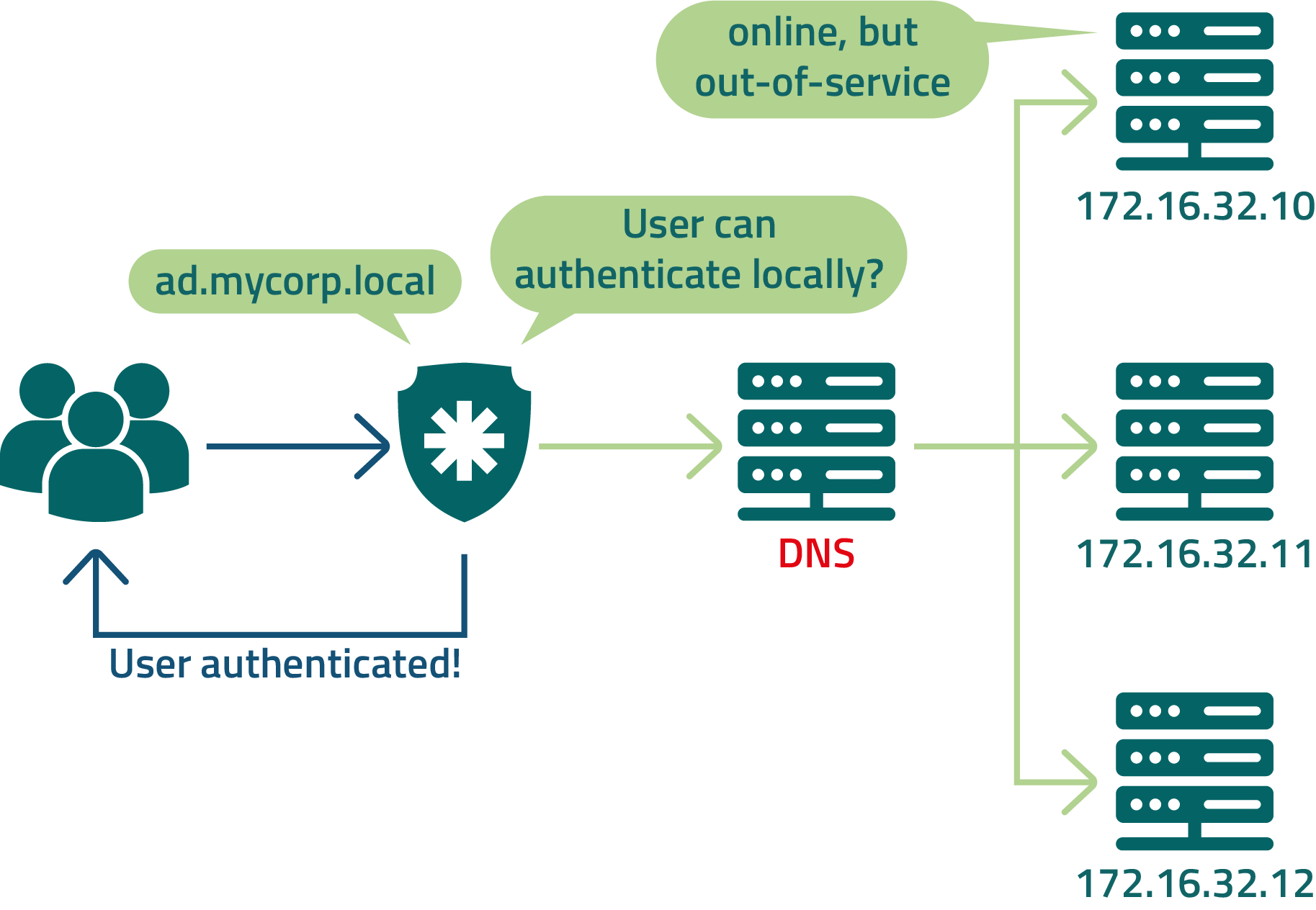
If DNS is offline as described in our first example, you can still configure senhasegura so that some trusted users can authenticate locally. This can be done on each user.
Configuring LDAP authentication servers in senhasegura
Before configuring the LDAP servers, it is necessary that these LDAP servers are already registered as devices in senhasegura , and that there is already a query credential to the LDAP registered. This credential will be used by senhasegura to perform user synchronization.
During the user authentication step, the user-provided credential itself will be used.
Within the Settings ➔ Authentication ➔ Active Directory ➔ Servers menu.
In the presented report you have access to all server records that are being queried by the LDAP authentication process if the Active Directory authentication provider is active.
By default senhasegura already has a template record. You can change or inactivate the default record.
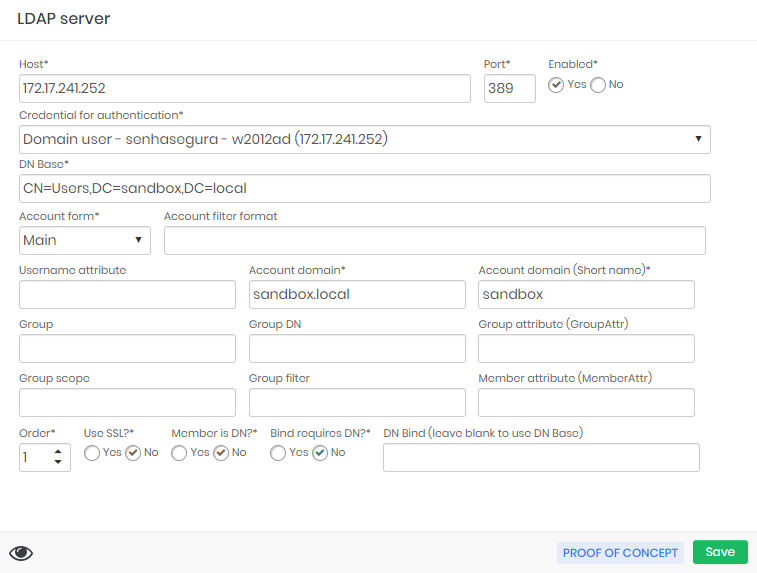
The registration form of an LDAP server contains several fields that serve to identify and filter the users that senhasegura can see. For a more comprehensive configuration you should be aware of the following fields:
Host: IP or hostname of the LDAP server;
Port: Port that the LDAP service is open for interaction;
Enabled: Status of this configuration;
Credential for authentication: The credential that is being used to perform user synchronization. Do not confuse with the credential used by the user for authentication;
DN Base: Address of AD elements that will serve as the basis for querying and synchronizing senhasegura ;
Account form: The users query can be performed using the following formats:
Username: just using username;
Backslash: using domain and username separated by a slash. Eg.
domain\userMain: using username and domain separated by at. Eg.
user@domain.netDN: Use DN filter for account identification;
Account domain: Full domain name;
Account domain (short name): Short domain name;
Order: Server query order under senhasegura authentication chain;
Use SSL: Flag this LDAP server have encryption by becoming an LDAPS;
Once registered and active, senhasegura can use this server to authenticate users.
Setting the authentication order for special users
Let's now configure fallback for local authentication of high-trust users. The rest of the users will respect the default order of the system.
You can refer to the default order of authentication in the Providers report. Exceptions are configured in the Providers by user report.
The admin user who is installed by default in senhasegura already has a record in this report showing that their authentication provider is only the Local and the first one.
For other users that need a secondary authentication provider, it is important to set the company's primary authentication first and keep the local authentication at last in the authentication chain.
Configuring group and user synchronization
With these previous settings, it is already possible for users to authenticate to the system if the user account is manually created inside senhasegura . But all registration management and user maintenance are not centralized. It is preferable that the user registration changes, which are being made on the LDAP server, be reflected in the user configuration and access groups of senhasegura .
senhasegura delivers the synchronization of LDAP users. The process is fully automated and requires a few steps, but you will need to pay attention to it.
Before we start setting up groups, you must be aware of how senhasegura Access Groups and Access Profiles work.
Another important information is that the senhasegura user synchronization service runs every three minutes.
Through the Group Synchronization menu, you have access to the working sync settings.
Each record is a different synchronization rule. And they may be querying the same LDAP server or different servers.
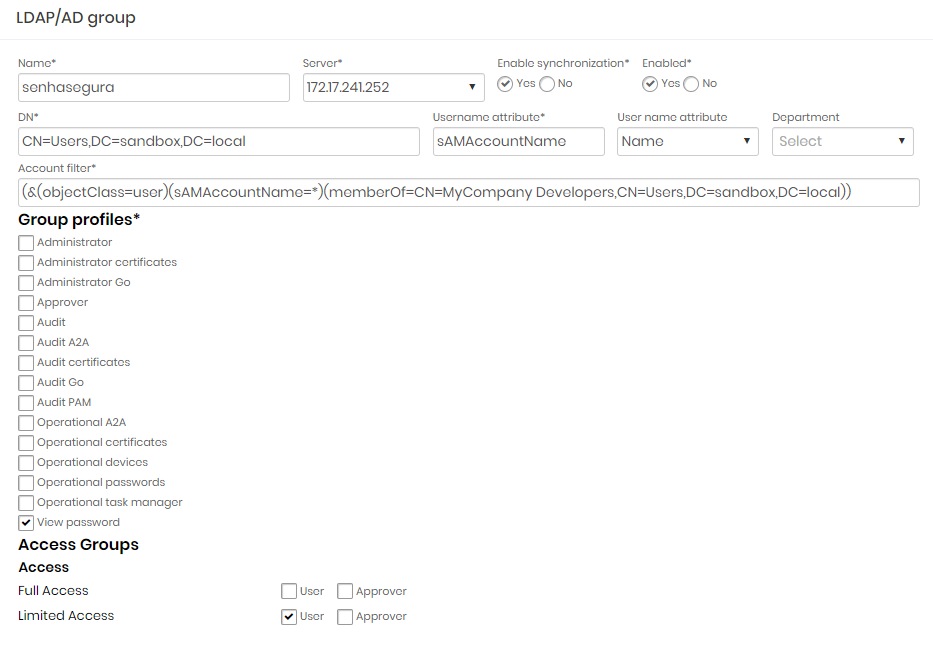
In the configuration form you will set a name to the rule, configure which server should be asked and which DN filter to use. It's interesting to keep sync down while you are setting up to avoid wrong users' creation.
Flag which Access Group and Access Profile each user will receive and save the configuration.
Perform the test to see if the filter used is showing the correct users. To do this, click the Synchronization test record action of the registered configuration.
On the synchronization test screen, validate that the DN and User Filter fields are populated in the same way you previously registered. If ok, click Simulate.
The field 'User Filter' supports up to 2048 characters.
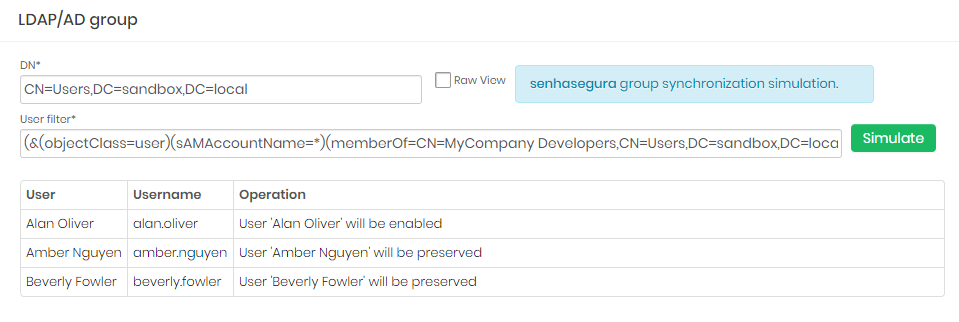
Notice the result. senhasegura will print the accounts that will be created, modified or maintained.
If you agree with the result presented, you can then enable synchronization by editing the configuration. Every three minutes senhasegura will perform synchronization, provisioning users, and recording the operation in the log reports Synchronized Users and Group Synchronization Log.
The Failure log report contains per-user authentication failure records. Use this report for a deeper diagnosis. By default, the user does not receive the detailed message from LDAP at the login failure, but in this report you have access to the original response.